How to capture TCP SYN, ACK and FIN packets with tcpdump
Last updated on September 7, 2020 by Dan Nanni
SYN, ACK or FIN flag set. How can I use tcpdump to capture TCP SYN, ACK, and/or FYN packets only?As a de-facto packet capture tool, tcpdump provides powerful and flexible packet filtering capabilities. The libpcap packet capture engine which tcpdump is based upon supports standard packet filtering rules such as 5-tuple packet header based filtering (i.e., based on source/destination IP addresses/ports and IP protocol type).
The packet filtering rules of tcpdump/libpcap also supports more general packet expressions, where arbitrary byte ranges in a packet are checked with relation or binary operators. For byte range representation, you can use the following format:
proto [ expr : size ]
proto can be one of well-known protocols (e.g., ip, arp, tcp, udp, icmp, ipv6). expr represents byte offset relative to the beginning of a specified protocol header. There exist well-known byte offsets such as tcpflags, or value constants such as tcp-syn, tcp-ack or tcp-fin. size is optional, indicating the number of bytes to check starting from the byte offset.
Using this format, you can filter TCP SYN, ACK or FIN packets as follows.
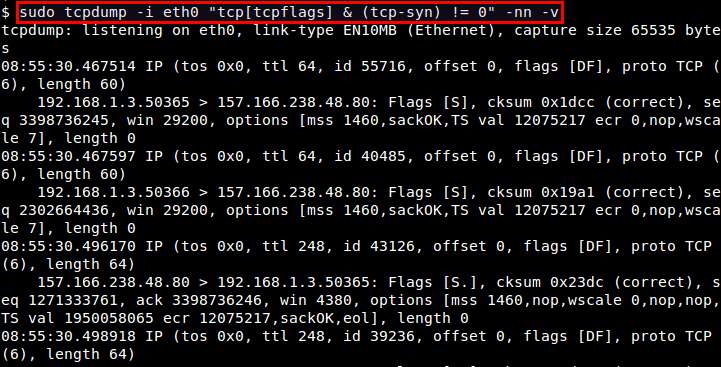
To capture only TCP SYN packets:
# tcpdump -i <interface> "tcp[tcpflags] & (tcp-syn) != 0"
To capture only TCP ACK packets:
# tcpdump -i <interface> "tcp[tcpflags] & (tcp-ack) != 0"
To capture only TCP FIN packets:
# tcpdump -i <interface> "tcp[tcpflags] & (tcp-fin) != 0"
To capture only TCP SYN or ACK packets:
# tcpdump -r <interface> "tcp[tcpflags] & (tcp-syn|tcp-ack) != 0"
Support Xmodulo
This website is made possible by minimal ads and your gracious donation via PayPal or credit card
Please note that this article is published by Xmodulo.com under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. If you would like to use the whole or any part of this article, you need to cite this web page at Xmodulo.com as the original source.
Xmodulo © 2021 ‒ About ‒ Write for Us ‒ Feed ‒ Powered by DigitalOcean

